Ear pressure can be uncomfortable, especially when flying, sick, or congested. The sensation of clogged or blocked ears often occurs due to Eustachian tube dysfunction, a small passage that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat and regulates air pressure. Knowing how to pop your ears safely can relieve discomfort, prevent pain, and improve hearing clarity. In this guide, we’ll explore multiple techniques for popping your ears, from simple swallowing and yawning exercises to medical-safe maneuvers. Whether you’re congested, recovering from a cold, or just landed from a flight, these expert tips will provide quick and reliable relief.
How to Pop Your Ears When Congested

When nasal passages and Eustachian tubes are congested, air cannot flow properly, leading to pressure buildup in the middle ear. Popping your ears in this situation requires careful methods to avoid pain or injury.
- Swallowing repeatedly: Swallowing activates the muscles that open the Eustachian tube, helping equalize pressure. Chewing gum or sucking on candy can enhance this effect by stimulating saliva production and repeated swallowing.
- Yawning intentionally: A deep yawn stretches the muscles near the Eustachian tube, temporarily opening it. Practicing wide yawns several times in a row often results in a satisfying “pop” sound.
- Valsalva maneuver carefully: Pinch your nose, close your mouth, and gently exhale to push air through the Eustachian tube. Avoid excessive force, as high pressure can damage the eardrum.
- Toynbee maneuver: Pinch your nose and swallow simultaneously. This method is often recommended by ENT specialists when congestion prevents regular popping.
- Nasal decongestants: Using short-term nasal sprays or oral decongestants can reduce swelling in the nasal passages, improving airflow to the Eustachian tube. Always follow package instructions to avoid side effects.
- Warm compress: Applying gentle warmth to the outer ear and sinus area can reduce inflammation and improve Eustachian tube function. This method is particularly useful if congestion is due to a mild sinus infection.
Also Read This:- What Does a Game Publisher Do? A Complete and In-Depth Explanation
How to Pop Your Ears When You Have a Cold

Colds often cause fluid buildup and inflammation in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, making ear pressure relief challenging. Gentle techniques are essential.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking water thins mucus, making it easier for the Eustachian tube to open naturally. Warm teas or broths can enhance comfort.
- Steam inhalation: Breathing in steam from a hot shower or bowl of water can moisten nasal passages, reduce congestion, and facilitate ear popping.
- Swallowing and chewing gum: Regular swallowing activates muscles connected to the Eustachian tube. Chewing sugar-free gum increases saliva flow and helps equalize pressure more effectively.
- Valsalva maneuver carefully: Pinch your nose and gently blow to push air into the middle ear. Avoid excessive force, especially during a cold, to prevent damaging the eardrum.
- Use a nasal saline spray: Saline sprays can flush out mucus and allergens, opening the nasal passages and improving Eustachian tube function.
- Elevate your head when resting: Keeping your head slightly elevated encourages sinus drainage and reduces ear pressure buildup during illness or sleep.
Also Read This:- What Does a Game Publisher Do? A Complete and In-Depth Explanation
How to Pop Your Ears After Flight

Airplane cabins create rapid pressure changes that often leave ears feeling blocked. Correct techniques prevent pain and long-term issues.
- Yawning and swallowing: Regular yawns or swallowing movements during takeoff and landing help equalize ear pressure.
- Valsalva maneuver: Pinch your nose and exhale gently to push air through the Eustachian tube. Perform slowly to avoid inner ear damage.
- Chewing gum or sucking candy: Both actions stimulate frequent swallowing, which naturally opens the Eustachian tube.
- Toynbee maneuver: Swallowing with your nose pinched is especially effective for sudden pressure changes in flight.
- Hydration: Drinking water helps thin mucus and facilitates Eustachian tube function, reducing blockage.
- Earplanes or pressure-regulating earplugs: Specialized earplugs slow pressure changes, making it easier for ears to adjust naturally during ascent and descent.
Also Read This:- What Does Media Upload Mean on Snapchat? A Complete User-Friendly Guide
How to Pop Your Ears in Seconds

Sometimes, ear pressure requires immediate relief. Fast, safe techniques can provide instant popping.
- Swallowing with a sip of water: Even a small sip can stimulate the swallowing reflex and instantly open the Eustachian tube.
- Quick yawning exercises: Force a deep yawn to stretch surrounding muscles and release pressure.
- Gentle Valsalva maneuver: Pinch your nose, close your mouth, and exhale lightly. Ensure the effort is moderate to avoid damage.
- Toynbee maneuver: Pinch your nose and swallow simultaneously to quickly equalize pressure.
- Neck and jaw movements: Rotating your jaw side-to-side or gently massaging the jaw muscles can help open the Eustachian tube.
- Ear tugging technique: Lightly pulling the outer ear while swallowing can sometimes help release trapped air.
Also Read This:- How to Make Ramen Chips: A Step-by-Step Guide to Crispy Homemade Snacks
How to Pop Your Ears Safely
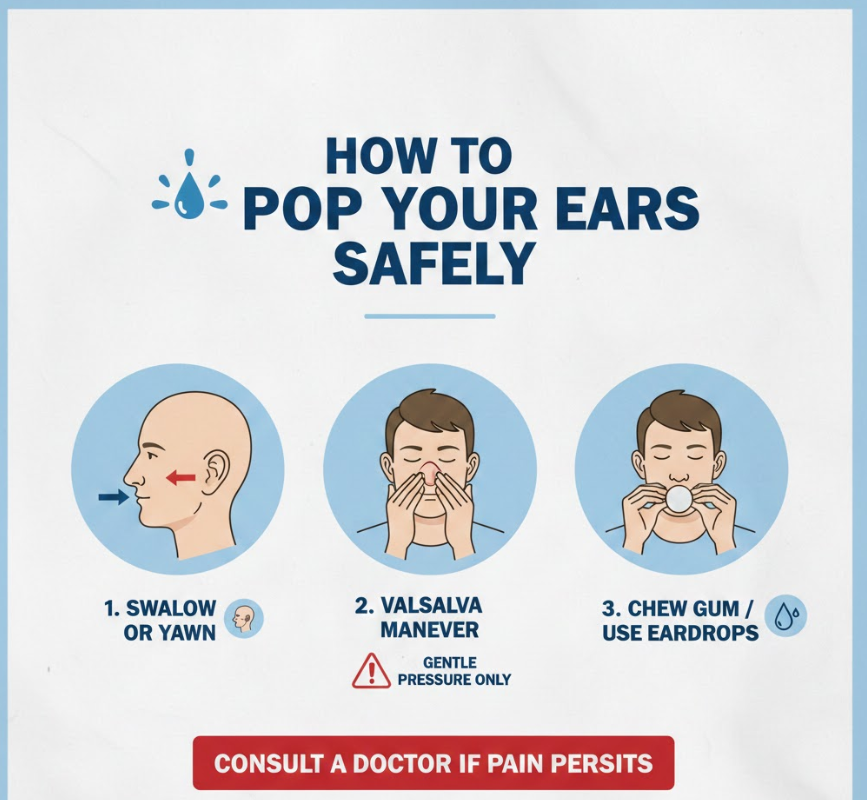
Safety is essential when attempting to pop your ears. Improper techniques can result in pain or permanent damage.
- Avoid excessive force: Never blow too hard during the Valsalva maneuver, as it can rupture the eardrum.
- Use gentle maneuvers first: Swallowing, yawning, and chewing are safest and effective for most cases.
- Limit decongestant use: Overuse of nasal sprays can cause rebound congestion. Follow instructions carefully.
- Avoid inserting objects: Cotton swabs or sharp objects should never be used inside the ear canal.
- Consult a doctor if pain persists: Severe ear pain or fluid discharge may indicate infection requiring medical attention.
- Monitor for dizziness or ringing: Any unusual symptoms may indicate inner ear issues; stop maneuvers immediately if these occur.
Also Read This:- How to Make Ramen Chips: A Step-by-Step Guide to Crispy Homemade Snacks
Tips for Maintaining Ear Health
- Keep ears clean but avoid cotton swabs inside the canal.
- Manage allergies and congestion to prevent Eustachian tube blockage.
- Hydrate regularly to reduce mucus viscosity.
- Use safe maneuvers like yawning, swallowing, or the Toynbee method for pressure relief.
- Seek medical advice if ear pain or pressure persists beyond a few days.
FAQs
Q1: Can I pop my ears if I have an ear infection?
No. Popping ears during infection can worsen pain or damage the eardrum. Consult a doctor.
Q2: Why do my ears feel clogged after flying?
Rapid pressure changes in airplane cabins cause the Eustachian tube to temporarily block, creating a clogged sensation.
Q3: Are there medications to help pop ears?
Decongestants or nasal sprays may help, but always use according to instructions and avoid long-term use without consulting a doctor.
Q4: Can children pop their ears safely?
Yes, gentle swallowing, yawning, and chewing are safe. Avoid forceful techniques like the Valsalva maneuver in very young children.
Visit For More Information go to:- Virtualsmagazine



